EVOLUTION OF HUMANS
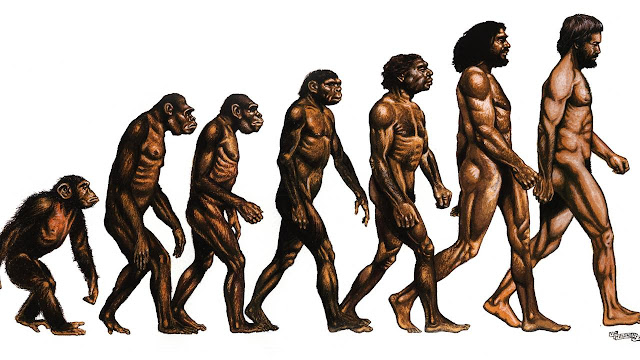
Human evolution is the protracted process of change by which people originated from apelike ancestors. Scientific evidence shows that the physical and behavioral qualities shared by all people began from apelike predecessors and developed over a time of roughly 6,000,000 years.
One of the most earliest defining human attributes, bipedalism the ability to walk on two legs evolved more than 4 million years ago. Other significant human attributes, for example, a large and complex brain, the ability to make and use tools, and the capacity with regards to language grew all the more as of late. Many propelled qualities including complex symbolic expression, art, and elaborate social diversity developed predominantly during the previous 100,000 years.
WHERE DID WE COME FROM?
AUSTRALOPITHECUS:
Species of the archaic human from the early Pleistocene of East and South Africa about 2.3 - 1.65 mya. Brain capacity differed from 500-900 cc. It is the least like present day people of all species in the genus homo. It is short in height 4 ft 3 inch and had long disproportional arms. They organized hunting and gathering. Their diet varied from fruits, leaves and occasionally small lizards.
They connected with the Early Stone Age Oldowan Stone Tool industry. also, utilized these tools primarily to butcher, skin creatures and pulverize bones but sometimes to saw and scrape wool and cut soft plants. They likewise depended on underground tubers and food sharing encouraged social holding.

HOMO HABILIS:
Meaning upright man, it's origins are in Africa but started to migrate to Eurasia, Georgia, India, Indonesia, China and Sri-Lanka. It was extinct some 1.9 million years ago. It was the first to exhibit a flat face, prominent nose and sparse body hair coverage. Brain capacity varied depending on the population ranging from 546-1251 cc and it's size ranged from 4 ft 9 in to 6 ft.
Additionally, these were the first hominins built for long-distance walking, pushing nomadic tribes into Asia and Europe.
They were the first to use fire, hunting and gathering in groups caring for the injured, seafaring, and possibly art making. They ate large game such as straight tasked elephants, rhinos, hippos among others. The lower cave of Zhoukoudian archaelogical sites worldwide. These were the first to make paleolithic tools like hand-axes.

HOMO HEIDELBERGENSIS:
They were the first to use fire, hunting and gathering in groups caring for the injured, seafaring, and possibly art making. They ate large game such as straight tasked elephants, rhinos, hippos among others. The lower cave of Zhoukoudian archaelogical sites worldwide. These were the first to make paleolithic tools like hand-axes.

HOMO HEIDELBERGENSIS:
H. heidelbergensis was scattered all through Eastern and Southern Africa (Ethiopia, Namibia, Southern Africa) just as Europe (England, France, Germany, Greece, Hungary, Italy, Portugal, Spain). The skulls of this species share features with both homo erectus and modern humans; its brain was close to as extensive as that of present day people.
They were presumably able to differentiate between a wide range of sounds. Dental wear examination recommends they were as likely to be right-handed as present day people. An archaeological site in Schöningen, Germany contained eight extraordinarily all around preserved about 400,000-year-old spears for hunting, and various other wooden tools.

HOMO NEANDERTHALS:
Neanderthals are an extinct species of hominids that were the closest relatives to modern human beings. They lived throughout Eurasia from about 400,000 until about 40,000 years ago, and they were adept at hunting large, Ice Age animals. They build cave hearths and crafted simple clothes like blankets, used medicinal plants.
They were presumably able to differentiate between a wide range of sounds. Dental wear examination recommends they were as likely to be right-handed as present day people. An archaeological site in Schöningen, Germany contained eight extraordinarily all around preserved about 400,000-year-old spears for hunting, and various other wooden tools.

HOMO NEANDERTHALS:
Neanderthals are an extinct species of hominids that were the closest relatives to modern human beings. They lived throughout Eurasia from about 400,000 until about 40,000 years ago, and they were adept at hunting large, Ice Age animals. They build cave hearths and crafted simple clothes like blankets, used medicinal plants.
Neanderthalenis was the first to use various cooking techniques like boiling, roasting and smoking. Resided in caves and moved seasonally.

CRO- MAGNON MAN:
European early modern humans during the Upper Paleolithic. It is taken to include fossils from throughout the last Glacial Maximus covering the period of 48.000 to 150.000 Gravettian, Solutrean, Magdelenian periods.
They were anatomically modern straight limb taller than Neanderthals. Specialized in cave and rock painting using manganese and iron oxides. Spears, spear-throwers and javelins were used when hunting big game. They pierced bone shells and teeth to make body ornaments.
There was construction of shelters in the form of rocks, clay, branches and animal hides. This group was the first to practice basketry and weaving.

HOMO SAPIENS:
Meaning the wise ones. Are highly intelligent primates that have become the dominant species on earth. They are exceptionally canny primates that have become the prevailing species on Earth. They are the only extant surviving members of the sub-tribe Hominina and along with chimpanzees, gorillas, and orangutans, they are a piece of the family Hominidae.
Early Homo sapiens continued to develop more specialized hunting techniques by inventing fishhooks, the bow and arrow, harpoons and more domestic tools like bone and ivory needles. These more specialized tools enabled them to widen their diet and create more effective clothing and shelter as they moved about in search of food.

Some percentage of people around the world believe that the Evolution of Humans began with Australopithecus while some percentage don't believe so.
What's your take on this post?
Do you agree with this subject or do you believe otherwise?
Write down your comments below.
Kindly subscribe to our blogpost to receive more great contents.

CRO- MAGNON MAN:
European early modern humans during the Upper Paleolithic. It is taken to include fossils from throughout the last Glacial Maximus covering the period of 48.000 to 150.000 Gravettian, Solutrean, Magdelenian periods.
They were anatomically modern straight limb taller than Neanderthals. Specialized in cave and rock painting using manganese and iron oxides. Spears, spear-throwers and javelins were used when hunting big game. They pierced bone shells and teeth to make body ornaments.
There was construction of shelters in the form of rocks, clay, branches and animal hides. This group was the first to practice basketry and weaving.

HOMO SAPIENS:
Meaning the wise ones. Are highly intelligent primates that have become the dominant species on earth. They are exceptionally canny primates that have become the prevailing species on Earth. They are the only extant surviving members of the sub-tribe Hominina and along with chimpanzees, gorillas, and orangutans, they are a piece of the family Hominidae.
Early Homo sapiens continued to develop more specialized hunting techniques by inventing fishhooks, the bow and arrow, harpoons and more domestic tools like bone and ivory needles. These more specialized tools enabled them to widen their diet and create more effective clothing and shelter as they moved about in search of food.

Some percentage of people around the world believe that the Evolution of Humans began with Australopithecus while some percentage don't believe so.
What's your take on this post?
Do you agree with this subject or do you believe otherwise?
Write down your comments below.
Kindly subscribe to our blogpost to receive more great contents.



This is a good primer on the topic as it focuses on several of the more well-known ancestors of humanity. I have to admit that I've never heard of Homo Heidelbergensis before, so I learned something in reading this. Well done!
ReplyDeleteWe're glad you learnt from this. Thank you
Delete